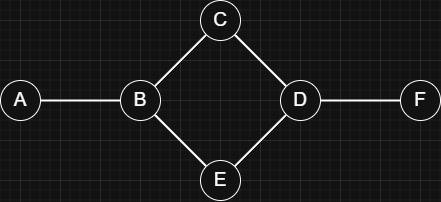
Graphs
Overview
A graph is a data structure used to represent relationships between things. It is made up of nodes (vertices) that represent the objects you care about and edges that represent the connections between them.
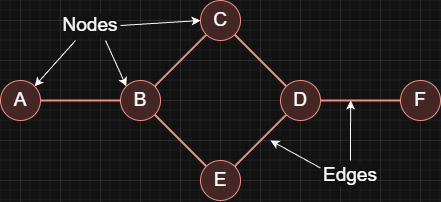
Types of Graphs
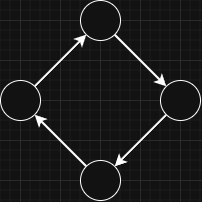
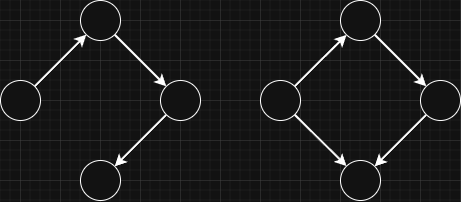
- Directed Graph:
Edges have a direction, so a connection goes from one node to another.

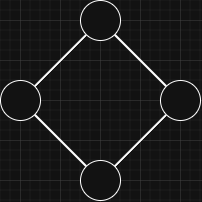
- Undirected Graph:
Edges have no direction, so the connection works both ways.
- Cyclic Graph:
Contains at least one cycle, meaning you can start at a node and return to it by following edges.
- Acyclic Graph:
Has no cycles, so you cannot return to a starting node by following edges.
- Unweighted Graph:
Edges do not have values, so all connections are treated as equal.
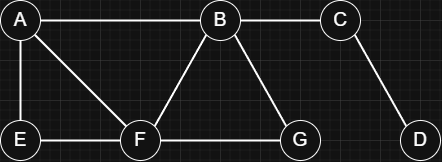 Here, the most efficient way from
Here, the most efficient way from AtoDisABCD(the shortest path). - Weighted Graph:
Edges have values (weights), such as distance, cost, or time.
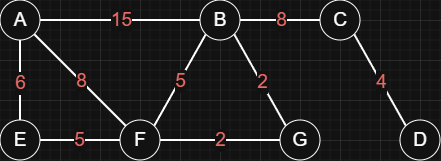 Here, the most efficient way from
Here, the most efficient way from AtoDisAFGBCD(the lowest total cost).
Code Representations
There are three common ways to represent a graph in code.
Example graph:
-
Edge lists.
A graph is stored as a plain list of edges. Each edge is a pair (
from,to) for unweighted graphs, or a triple (from,to,weight) for weighted graphs.const edgeList = [ ['A', 'B'], ['B', 'C'], ['B', 'E'], ['C', 'D'], ['D', 'E'], ['D', 'F'], ]; -
Adjacency matrices.
A graph is stored as a 2D grid of values. The cell at (
i,j) indicates whether there is an edge from nodeito nodej(often0/1), or stores the edge weight in weighted graphs.const adjMatrix = { A: { A: 0, B: 1, C: 0, D: 0, E: 0, F: 0 }, B: { A: 1, B: 0, C: 1, D: 0, E: 1, F: 0 }, C: { A: 0, B: 1, C: 0, D: 1, E: 0, F: 0 }, D: { A: 0, B: 0, C: 1, D: 0, E: 1, F: 1 }, E: { A: 0, B: 1, C: 0, D: 1, E: 0, F: 0 }, F: { A: 0, B: 0, C: 0, D: 1, E: 0, F: 0 }, }; -
Adjacency lists.
A graph is stored as a mapping from each node to its neighbors. Each key is a node, and its value is a list of directly connected (outgoing) nodes (or pairs like (
neighbor,weight) for weighted graphs).const adjList = { A: ['B'], B: ['A', 'C', 'E'], C: ['B', 'D'], D: ['C', 'E', 'F'], E: ['B', 'D'], F: ['D'], };