Linked List
Overview
A linked list is a data structure made of nodes where each node holds a value and a reference to the next node. The nodes form a chain in memory which allows the list to grow or shrink easily by adjusting references.
| Operations | Complexity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Access/Edit | O(n) | Reaching a position requires sequential node traversal. |
| Access/Edit first & last | O(1) | Head and tail pointers give direct access to ends. |
| Insert | O(n) | Traversal is required to reach the insertion point. |
| Insert front & end | O(1) | Head or tail pointer is updated directly. |
| Remove | O(n) | Traversal is required to locate the node. |
| Remove first | O(1) | Head pointer is updated directly. |
Background
Linked lists can be formed with one or two references per node, creating singly or doubly linked structures.
-
Singly Linked List:
- Value: The data stored in the node.
- Next: A reference to the next node in the list.
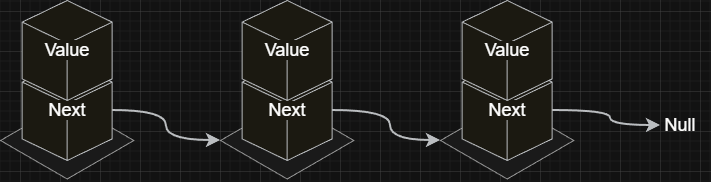
-
Doubly Linked List:
- Value: The data stored in the node.
- Next: A reference to the next node in the list.
- Prev: A reference to the previous node in the list.
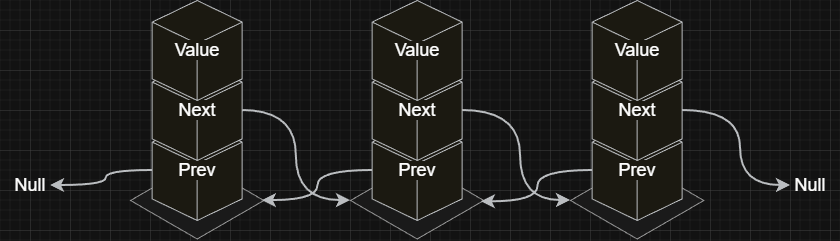
In doubly linked lists, removing the last node is
O(1)because its previous node is directly reachable.
Implementation
class ListNode {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.size = 0;
}
// Access:
get(index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
throw new Error('invalid index');
}
let currNode = this.head;
for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
currNode = currNode.next;
}
return currNode;
}
// Insert front:
prepend(value) {
const newNode = new ListNode(value);
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
// Insert end:
append(value) {
const newNode = new ListNode(value);
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else {
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
// Insert
insertAt(index, value) {
if (index <= 0) {
this.prepend(value);
} else if (index >= this.size) {
this.append(value);
} else {
const newNode = new ListNode(value);
const parent = this.get(index - 1);
newNode.next = parent.next;
parent.next = newNode;
this.size++;
}
}
// Remove:
deleteAt(index) {
if (this.head === null) {
throw new Error('list is empty');
}
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
throw new Error('invalid index');
}
if (index === 0) {
this.head = this.head.next;
if (this.head === null) {
this.tail = null;
}
} else {
const parent = this.get(index - 1);
parent.next = parent.next.next;
if (index === this.size - 1) {
this.tail = parent;
}
}
this.size--;
}
// (optional) Only to make the list easier to view:
toArray() {
const list = [];
let currNode = this.head;
while (currNode !== null) {
list.push(currNode.value);
currNode = currNode.next;
}
return list;
}
}Usage:
const myList = new LinkedList(); myList.append('one'); myList.append('two'); myList.append('three'); myList.insertAt(1, 'four'); console.log(myList.toArray()); // (4) ['one', 'four', 'two', 'three'] myList.prepend('five'); myList.deleteAt(2); console.log(myList.toArray()); // (4) ['five', 'one', 'two', 'three']