Binary Trees
Overview
A binary tree is a tree structure where each node can have up to two children, known as left and right children. It is called a "binary" tree because the branching factor of each node is limited to two.
Types of Binary Trees
- Full Binary Tree:
A full binary tree is a binary tree in which every node has either zero or two children.
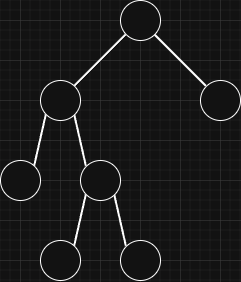
- Perfect Binary Tree:
A perfect binary tree is a binary tree in which every level is completely filled and all leaf nodes are on the same level.
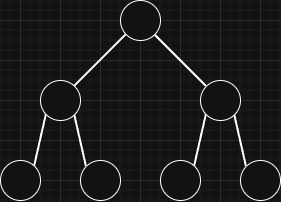
- Node count in each level:
2^curr_level - Last level node count:
nodes_in_all_previous_levels + 1 - Total node count:
2^(height + 1) - 1
- Node count in each level:
- Complete Binary Tree:
A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which all levels are filled except possibly the last level. The last level is filled from left to right.
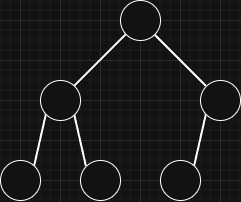
- Balanced Binary Tree:
A balanced binary tree is a binary tree in which the heights of the left and right subtrees of any node differ by at most one.
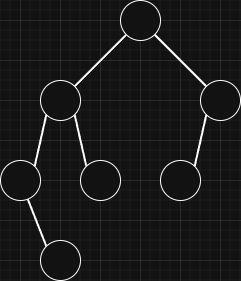
The tree can become unbalanced depending on inserted and deleted items. In an unbalanced tree, lookup, insert, and delete operations can take
O(h)time because the tree starts to behave like a linked list. To address the issue there are structures like AVL Trees ↗ or Red Black Trees ↗. These structures perform extra rotations after insert or delete operations to keep the tree balanced.